The Red Sea is a pivotal geopolitical region with a rich history and significant importance in contemporary global affairs. It channels 30% of global container traffic. According to the World Bank Document, the escalating conflict around the Red Sea crisis has an intensifying impact and far-reaching consequences on international stability.
Recently, we have understood that this crisis has emerged as a pressing concern, affecting regional stability and the broader global landscape. Furthermore, the conflict has contributed to a dramatic slump in maritime activity.
This article aims to illuminate the complexities of the Red Sea crisis and its far-reaching implications, encouraging readers to understand the intricate dynamics at play.
Critical Insights into the Crisis

1. Economic Implications for Global Trade
The Red Sea crisis has significant ramifications for global trade, particularly concerning shipping routes. The Red Sea is a crucial link between Bab El-Mandeb in the Gulf of Aden and the Suez Canal, facilitating the passage of nearly one-third of the world’s container cargo ships.
Strategically located between Africa and the Arabian Peninsula, Bab El-Mandeb accounts for approximately 13% of international trade by volume and nearly 30% of global container traffic transported between Europe and Asia.
However, in the wake of the conflict, there has been a notable decline in global maritime traffic through the Red Sea, with a reported decrease of 1.3% in international trade as of December 2023.
Disruptions lead to delays and increased shipping costs, ultimately impacting consumers worldwide. Recent reports indicate that shipping delays have surged by over 25% due to increased military activity and piracy threats, underscoring the crisis’s economic consequences.
2. Security Risks and Maritime Threats
The security landscape in the Red Sea is fraught with challenges, including the threat of piracy and military conflicts.
These risks jeopardize the safety of vessels traversing these waters and pose significant concerns for shipping companies and global supply chains.
The resurgence of piracy, particularly off the coasts of Somalia and Yemen, has compelled shipping firms to reconsider routes and increase security measures, further driving up operational costs.
3. The Role of International Diplomacy
Efforts by global powers to mediate and resolve the Red Sea crisis have been ongoing. Diplomatic initiatives aim to foster dialogue among conflicting parties and de-escalate tensions.
The involvement of organizations such as the United Nations and the African Union highlights the importance of multilateral approaches in addressing complex geopolitical issues.
The outcomes of these diplomatic efforts will significantly shape future scenarios, either stabilizing the region or exacerbating existing conflicts.
The Broader Impact on Global Stability

The Red Sea crisis is not an isolated issue; it is intricately connected to broader geopolitical trends, including shifts in power dynamics and emerging security threats. Local conflicts can have profound global repercussions, affecting everything from trade to international relations.
By recognizing the interconnectedness of these issues, we can better understand the need for proactive measures to address potential instability.
Here are the impacts of the Red Sea crisis on global stability:
1. Rerouting
This substantial decline in maritime traffic has compelled significant shipping companies to suspend or reroute their shipping lines, opting to navigate South Africa’s Cape of Good Hope, a longer, more costly, and time-intensive trade route.
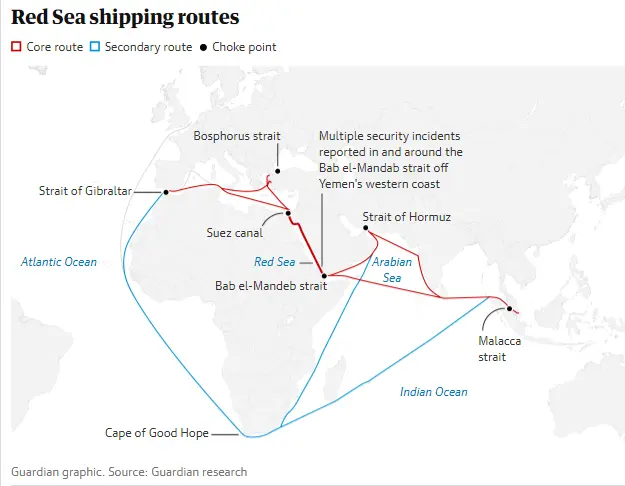
Source: The Guardian
2. Shipping Delays
Based on data from Infor Nexus, the most pronounced delays are occurring in shipments originating from Asian ports destined for Western Europe and the United States East Coast.
Routes from Asia to Germany have been particularly impacted, with transit times increasing by an extraordinary 55%, resulting in an average delay of 12 days. Likewise, shipments headed for New York and other East Coast ports face delays of up to 11 days.
3. Increased Costs
Uncertainty regarding the security of the Bab el-Mandeb Strait has led to a significant rise in insurance premiums and shipping costs for maritime companies.
Marine war risk premiums have surged nearly fiftyfold since the onset of the conflict, reaching up to 1% of a ship’s value. For instance, a vessel carrying goods valued at $100 million incurs an additional $700,000 in premiums.
Furthermore, rerouting around the Cape of Good Hope adds substantial fuel costs, compounding the financial burden. This disruption will likely impact the global economy, forcing retailers to absorb the increased costs or raise consumer prices, potentially undermining the fragile economic recovery.
4. Supply chain resilience and Redundancy
The current crisis highlights the necessity of resilience and redundancy in global supply chains. Companies are reassessing their reliance on specific routes and suppliers, exploring alternative options to mitigate risks associated with the Red Sea crisis.
Organizations that prioritize domestic sourcing have proven more resilient to the disruptions. Given that the Red Sea is a critical transit point, any disturbances in shipment flow can have far-reaching consequences for global markets.
Increased costs are particularly burdensome for retailers dependent on global sourcing. They are mostly struggling to obtain essential parts and goods amid the ongoing crisis.
Also Read: Ukraine Invasion Heightens Marine Risk in Asia
The Red Sea crisis presents a complex tapestry of historical tensions, economic implications, security risks, and humanitarian concerns. We encourage you to stay informed about such pressing global issues and consider their implications for businesses and society.
For those looking to navigate the challenges associated with global instability, engage with Azure Risk, a trusted business insurance broker in Hong Kong.
We can provide valuable insights and resources. Explore solutions to manage risks and prevent losses in your business. Get insured today!